A QUICK GUIDE: ULTRASOUND GUIDED NERVE BLOCKS
Ultrasound Machine and Image Acquisition Scanning Preparation
- Obtain written informed consent for the block - AORA WRITTEN CONSENT FORM
- Re-examine the patient before administering the block
-
Checklist ticked before the block --(anaesthesiologist and nurse to be present) AORA CHECKLIST
- - Ensure we have correct patient/block and marked site/side of block
- - Check Documents and Equipment before initiating the procedure
- - I.V cannula secured before performing the block
- - Minimum ASA standard monitoring (pulse oxymeter, NIBP, ECG) started
-
Ergonomics- Ultrasound machine should be in direct line of sight of the anaesthesiologist performing the block
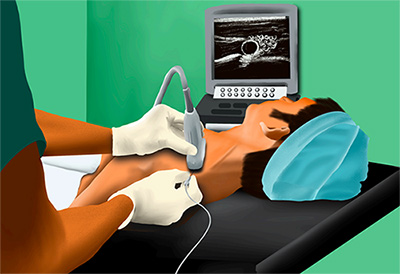
(Figure 1) - Selection of Pre-Set in certain machines to better visualize that structure (eg: Nerves/ Musculoskeletal/Vascular)
- Probe selection - High frequency probe (13-6 MHz) for superficial nerves/structures and Low frequency probe (5-2 MHz) for deeper nerves/structures and neuraxial blocks
- Tegaderm, Cling Wrap or Camera Cover wrapped around the probe for sterility
- Oxygen administration via ventimask /nasal prongs
- I.V. sedation like Midazolam /Fentanyl I.V. before initiating the block, but after finishing timeout/checklist
- Maintenance of strict asepsis during the block procedure - AORA STERILITY PRECAUTIONS
- Skin infiltration with 1% Lignocaine 1 min before inserting the needle; at the site of needle entry
- Probe holding: Pen holding method is preferable for most blocks
- At end of procedure- probe should be cleaned with Soap and water #FIGURE 1. Ergonomics with Ultrasound Machine/Probe (line diagram)
Image Optimisation
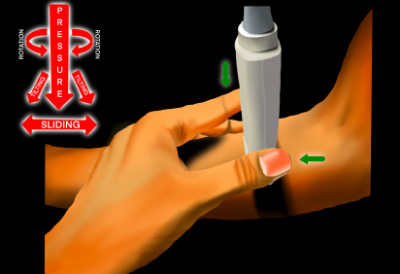
The following movements of the probe can be utilized for optimization of image:
Transducer Movements:
- Sliding
- Tilting
- Rocking
- Rotation
- Compression
Needle Approaches
- In Plane - Whole length of the needle is visualized
- Out of Plane - Only needle tip is visualized
Clinical Pearls
- Optimize the image by setting the appropriate focus, depth and gain
- Focus the target in centre of the screen
- Ensure that the skin sterilizing solution has dried, before inserting the needle for block, as contact of sterilizing solution with the nerve can lead to nerve injury (neuropraxia /neurotemesis /axonotemesis)
- Incremental injection of Local Anaesthetic in 2-3 ml aliquots after repeated aspiration
- Stop administration of perineural drug, if the patient complains of pain during injection; as it can be a feature of intraneural injection of drug and lead to nerve injury
- When using peripheral nerve stimulator, never inject the drug, if muscle contraction occurs at current less than 0.3 MA; as it can be a feature of intraneural (intrafascicular) administration of drug and cause nerve injury
- Scan with the Colour Doppler while doing Brachial Plexus Block (especially Interscalene and Infraclavicular blocks); to avoid inadvertent intravascular injection
These practical tips decrease the potential complications, making ultrasound guided regional anaesthesia a safer technique. Acquisition of a better image improves the success rate of the block.
| Dr Kapil Gupta | Dr Neha Singh | Dr Rammurthy |
|---|---|---|
| Professor, Anesthesiology, V.M.M.C & Safdarjung Hospital, New Delhi |
Additional Professor, Anesthesiology, AIIMS, Bhubaneshwar |
Consultant Anaesthesiologist, Axon Anaesthesia Associates, Bangalore |

